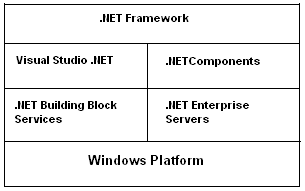
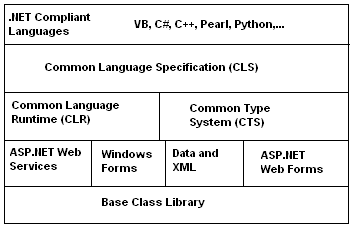
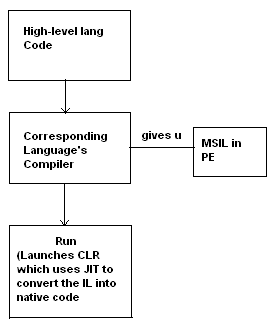
Recursive Program List in C:-
C Program to find the Length of the String using Recursion
C Program for Depth First Binary Tree Search using Recursion
C Program to Traverse the Tree Recursively
C Program to Reverse a Stack using Recursion
C Program to Implement Selection Sort Recursively
C Program to Perform Matrix Multiplication using Recursion
C Program to Input Few Numbers & Perform Merge Sort on them using Recursion
C Program to find the Nth Fibonacci Number using Recursion
C Program to find the Biggest Number in an Array of Numbers using Recursion
C Program using Recursion to Search an Element in Array
C Program to Search for an Element in the Linked List using
Recursion
C Program to Reverse the String using Recursion
C Program to Display the Nodes of a Linked List in Reverse
using Recursion
C Program Count the Number of Occurrences of an Element
in the Linked List using Recursion
C Program to Display all the Nodes in a Linked List using
Recursion
C Program to find Sum of Digits of a Number using Recursion
C Program find the Length of the Linked List using Recursion
C Program to find Reverse of a Number using Recursion
C Program to find Sum of N Numbers using Recursion
C Program to find HCF of a given Number using Recursion
C Program to find Power of a Number using Recursion
C Program to Perform Quick Sort on a set of Entries from a
File using Recursion
C Program to Solve Tower-of-Hanoi Problem using Recursion
C Program to Copy One String to Another using Recursion
C Program to find whether a Number is Prime or Not using
Recursion
C Program to find the Factorial of a Number using Recursion
C Program to find LCM of a Number using Recursion
C Program to find Product of 2 Numbers using Recursion
C Program to Check whether a given String is Palindrome or
not using Recursion
C Program to find GCD of given Numbers using Recursion
C Program to Perform Binary Search using Recursion
C Program to Print Binary Equivalent of an Integer using
Recursion
C Program to Print the Alternate Nodes in a Linked List using
Recursion
C Program to Convert a Number Decimal System to Binary
System using Recursion
C Program to find the First Capital Letter in a String using
Recursion
C Program to Search an Element in a Tree Recursively